
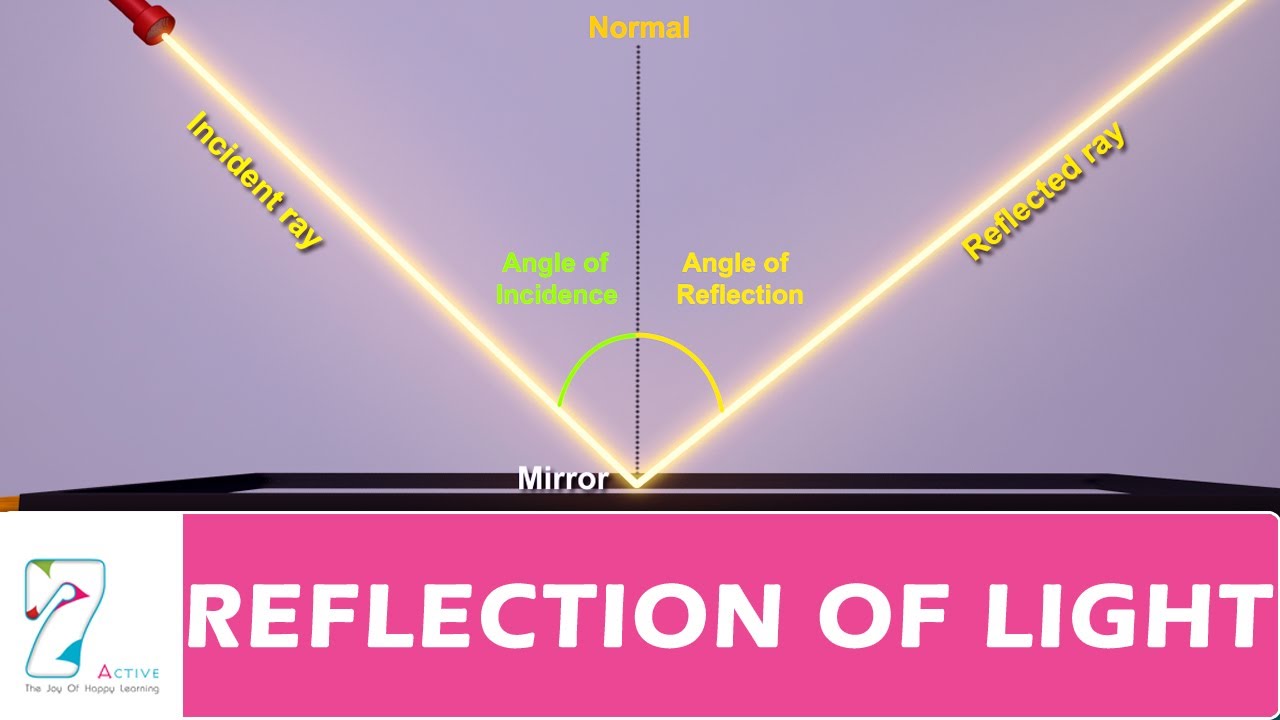

Mirror images can be photographed and videotaped by instruments and look just as they do with our eyes (which are optical instruments themselves). Although these mirror images make objects appear to be where they cannot be (like behind a solid wall), the images are not figments of your imagination. If the mirror is on the wall of a room, the images in it are all behind the mirror, which can make the room seem bigger. The angles are such that the image is exactly the same distance behind the mirror as you stand in front of the mirror. (ii) The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence. (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and. Reflection also occurs at the surface of transparent media, such as water or glass.
ANGLE OF REFLECTION MIRRORS SKIN
We see the light coming from a direction determined by the law of reflection. Reflection is enhanced in metals by suppression of wave propagation beyond their skin depths. When you see yourself in a mirror, it appears that the image is actually behind the mirror ( (Figure)). Either way (light clock or mirror), the resultant beam would be vertical. (credit c: modification of work by Diego Torres Silvestre) A variation would be to shine a horizontal light beam at a 45 degree mounted mirror in a moving ship. (c) Moonlight is spread out when it is reflected by the lake, because the surface is shiny but uneven. Only the observer at a particular angle sees the reflected light. (b) A mirror illuminated by many parallel rays reflects them in only one direction, because its surface is very smooth. You can access the Help page from within the mission by tapping on the Help Me! icon (textbook).(a) When a sheet of paper is illuminated with many parallel incident rays, it can be seen at many different angles, because its surface is rough and diffuses the light. What is the relationship between the angle measurements for an incoming light ray and an outgoing light ray?Įach Question Group has its own Help page with information specific to the question.Reflected from two mirrors at right angle, the light goes directly back for any incident angle. What is the definition of the angle of reflection? Intensity of reflected light increases with the angle.What is the definition of the angle of incidence?.If light is reflected, the light rays leave a surface at the same angle. The light can be bounced (reflected), bent (refracted), or absorbed.

When light meets the surface of an object, three things can happen. The Physics Classroom, Reflection and Mirrors Unit, Lesson 1, Part c Light is a type of energy that we can see, and mirrors are a great way to teach the properties of light. If you are not familiar with this topic, then you should first learn about the topic using our written Tutorial or our Video Tutorial: The student should be able to apply the law of reflection in order to identify the angle of incidence and reflection if given other angle information.The student should be able to identify and apply the definitions of the angle of incidence, the angle of reflection, incident ray and reflected ray.You can think of light as being a kind of wave, similar to the waves in the ocean. Below you can see waves of light reflecting off a mirror. Light reflects from a mirror at the same angle as it arrives. You must answer one question from each Question Group to complete the mission. The learning outcomes for this mission are. When you see the image of your face in a mirror, you are seeing the reflection of light from your face. The mission consists of 34 questions organized into 9 Question Groups. Mission RM1 pertains to the law of reflection, the terminology associated with it, and its use in predicting the value of the angle of reflection. Minds On Physics » Reflection and Mirrors » Law of Reflection Mission RM1: Law of Reflection


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
